Growth of Islamic Finance to Facilitate Financial Inclusion
Article Overview
The growth of the Islamic finance industry offers important potential benefits, the IMF stated in its IMF Research June 15 bulletin.
The IMF stated the sector could facilitate financial inclusion by increasing access to banking services to underserved Muslim populations. Furthermore the risk-sharing characteristics of Islamic financial products can facilitate access to finance by small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) whilst the asset backed nature of Sukuk makes them suitable for infrastructure financing that can help spur economic development, including creating an enabling environment for private sector investment.
However, to realize the potential and to safeguard financial stability, countries need to adapt their regulatory, supervisory, and consumer protection frameworks to the specificities of Islamic finance; to develop Shari’ah-compliant financial markets and monetary instruments; and to build an enabling environment for Sukuk market development.
Industry Growth Trends
The IMF views Islamic finance assets as having reached $1.8 Trillion by end of 2014, a valuation that is consistent with statistics provided by industry bodies such as the IFSB.
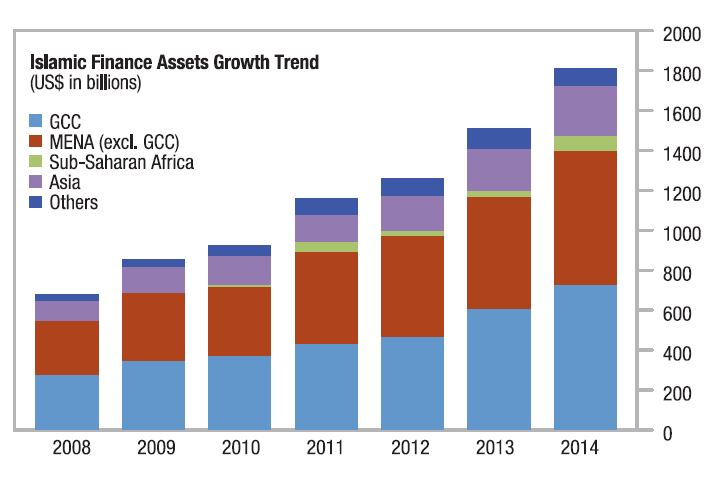
IMF Data – Growth trends in Islamic finance broken down into per sector.
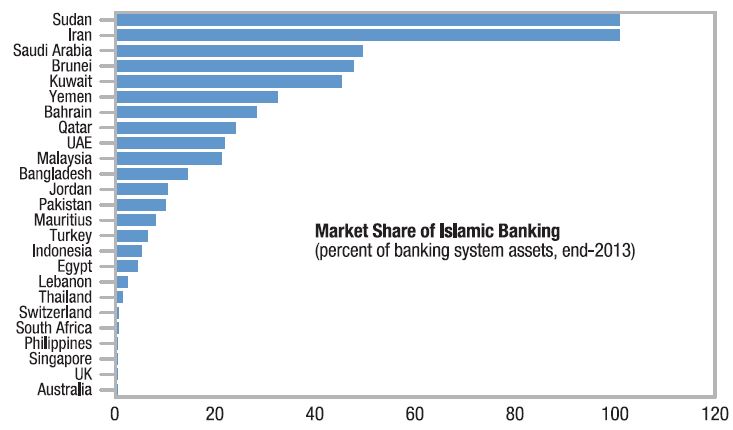
Sudan and Iran maintain large domestic markets consistent with values of Sharia and Islamic Banking.
Global Sukuk Issuance hit a record in 2012 with the IMF suggesting the upward trend remains the direction of travel. The IMF stated whilst the Sukuk market has registered rapid growth in value and the issuer base has broadened, the markets for Sukuk are still neither deep nor liquid, and most issues of Sukuk are asset based and not asset backed. Issuance also takes place without a comprehensive strategy to develop the domestic market.
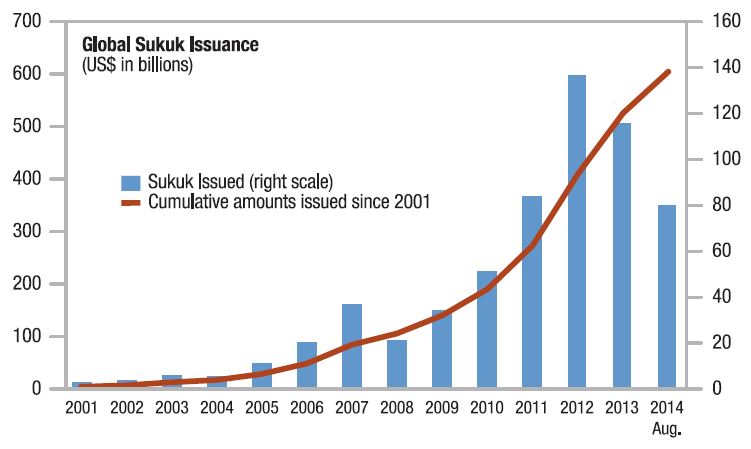
Global Sukuk Issuance
Regular sovereign issuance, and at different maturities, is critical for deepening the market and establishing a yield (or Sukuk) curve that could provide a benchmark for corporate Sukuk. Increased sovereign issuance should also be underpinned by sound public financial management (PFM), and attention should be given to the accounting and statistical treatment of Sukuk instruments, which are currently largely overlooked in existing international standards.